
DOL is one metric that can be used to access the risk profile of a company. A high DOL means that a company is more exposed to fluctuations in economic conditions and business cycles. However, xero hq in the short run, a high DOL can also mean increased profits for a company. Thus, it is important for investors to carefully consider a company’s DOL when making investment decisions.
How Does Cyclicality Impact Operating Leverage?
- This section will use the financial data from a real company and put it into our degree of operating leverage calculator.
- This ratio summarizes the effects of combining financial and operating leverage, and what effect this combination, or variations of this combination, has on the corporation’s earnings.
- DOL is an important ratio to consider when making investment decisions.
From Year 1 to Year 5, the operating margin of our example company fell from 40.0% to a mere 13.8%, which is attributable to $100 million fixed costs per year. On the other hand, if the case toggle is flipped to the “Downside” selection, revenue declines by 10% each year, and we can see just how impactful the fixed cost structure can be on a company’s margins. The direct cost of manufacturing one unit of that product was $2.50, which we’ll multiply by the number of units sold, as we did for revenue. Upon multiplying the $2.50 cost per unit by the 10mm units sold, we get $25mm as the variable cost.
What are the limitations of using DOL?
The more fixed costs there are, the more sales a company must generate in order to reach its break-even point, which is when a company’s revenue is equivalent to the sum of its total costs. That’s mean operating leverage relies upon the existence of fixed operating costs in order to generate the revenue stream of a company. It means one percentage change in sales leads to more percentage change in operating income. For example, if the ratio is equal to 2, 1% percentage change in the sale will lead to 2% (1% x 2) change in operating income. Management needs to pay much attention to the sale to maintain a high level of profit. On the other hand, the lower ratio shows the small impact of the sales changes over the operating income.
Operating Leverage Analysis Example
If you try different combinations of EBIT values and sales on our smart degree of operating leverage calculator, you will find out that several messages are displayed. To determine whether your business has a high or a low DOL, examine your organisation’s performance compared to other organisations. However, you should not be referring to every industry as some might have higher fixed costs than other industries. DFL refers to the sensitivity of the cash flows available to the owners of a company when operating income changes. Undoubtedly, the company benefits in the short run from high operating leverages in most cases.
Example: DOL
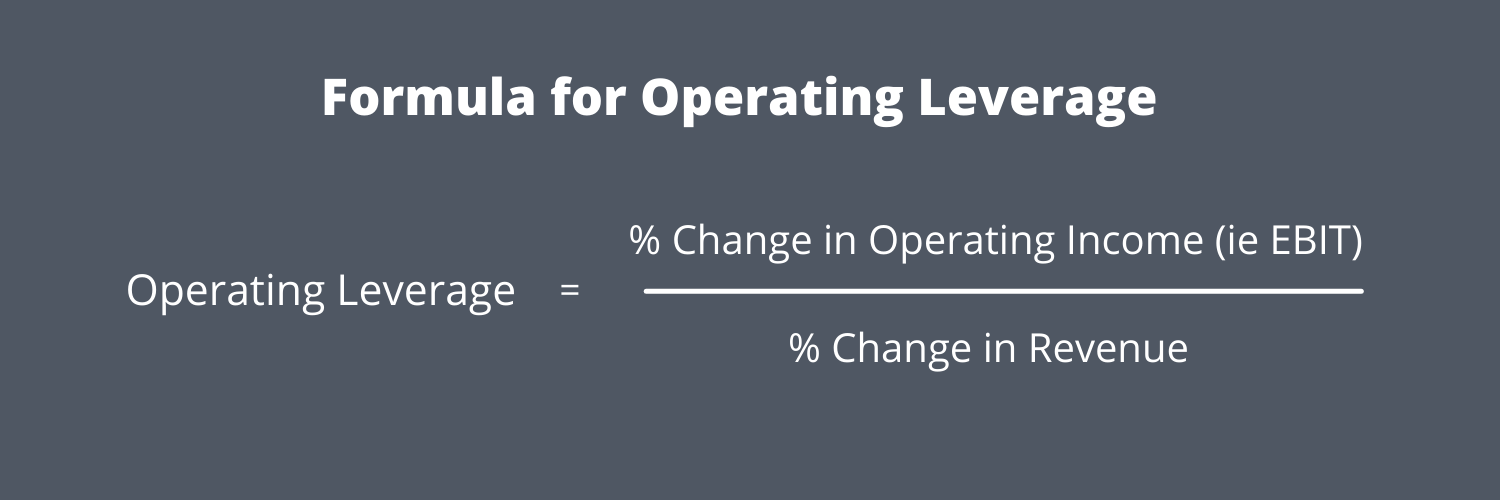
This ratio summarizes the effects of combining financial and operating leverage, and what effect this combination, or variations of this combination, has on the corporation’s earnings. Not all corporations use both operating and financial leverage, but this formula can be used if they do. A firm with a relatively high level of combined leverage is seen as riskier than a firm with less combined leverage because high leverage means more fixed costs to the firm. The higher the degree of operating leverage (DOL), the more sensitive a company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) are to changes in sales, assuming all other variables remain constant. The DOL ratio helps analysts determine what the impact of any change in sales will be on the company’s earnings.
Sale decreased by 30%
Many small businesses have this type of cost structure, and it is defined as the change in earnings for a given change in sales. Other company costs are variable costs that are only incurred when sales occur. This includes labor to assemble products and the cost of raw materials used to make products.
The management of XYZ Ltd. wants to calculate the current degree of operating leverage of its company. Here, the variable cost per unit is Rs.12, while the total fixed cost is Rs.1,00,000. When there are changes in the proportion of fixed and variable operating costs, thus the changes in sales quantity will lead to the changes in the degree of operating leverage. The DOL is greater than 1 indicates that the operating leverage exists. It means that the change in sales leads to a more earnings before interest and taxes after accounting for both variable and fixed operating costs.
If a company has low operating leverage (i.e., greater variable costs), each additional dollar of revenue can potentially generate less profit as costs increase in proportion to the increased revenue. Intuitively, the degree of operating leverage (DOL) represents the risk faced by a company as a result of its percentage split between fixed and variable costs. Companies with a high degree of operating leverage (DOL) have a greater proportion of fixed costs that remain relatively unchanged under different production volumes. In fact, operating leverage occurs when a firm has fixed costs that need to be met regardless of the change in sales volume.